In the complex mechanical systems of modern automobiles, the automatic transmission (AT) is undoubtedly one of the most technologically advanced and precisely structured components. Within this intricate power delivery system, the planetary gear set plays a vital role—acting as the "brain" and "joints" of the transmission, it is the core mechanical structure enabling automatic gear shifting, speed regulation, and torque adjustment. This article will provide an in-depth analysis of the working principles, structural composition, application scenarios, technical advantages, challenges, and future trends of automotive planetary gears. Combined with diagrams, it offers a comprehensive understanding of this "intelligent core" in modern automotive engineering.
I. What is a Planetary Gear? — Structure and Naming Origin
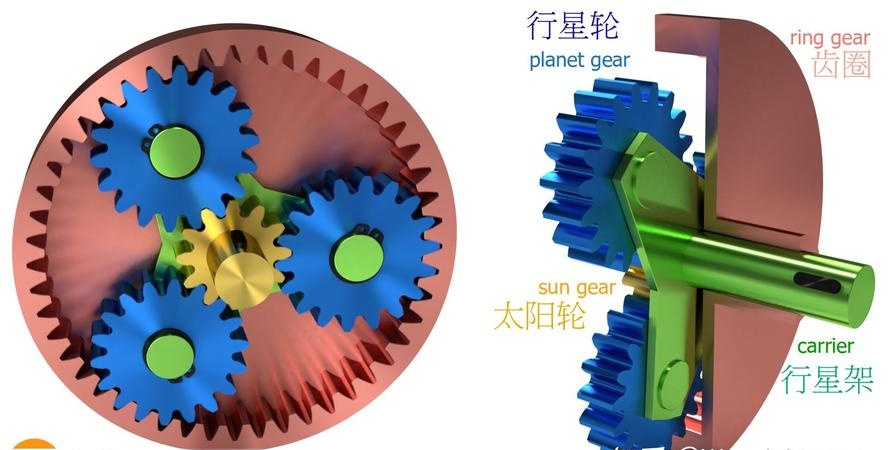
The planetary gear set, also known as a "planetary gear train" or "epicyclic gear train," is a specialized gear system where multiple gears work in coordination. Its name derives from its structural resemblance to the solar system:
- Sun Gear: The central gear, akin to the sun.
- Planet Gears: Multiple smaller gears that rotate around the sun gear, like planets.
- Planet Carrier: A支架结构 that supports the planet gears, allowing them to rotate on their own axes (spin) and revolve around the sun gear (orbit).
- Ring Gear (Annulus Gear): The outermost ring with internal teeth that mesh with the planet gears, resembling an orbit.
These four core components together form a basic planetary gear unit. By fixing, driving, or releasing any one of these components, the motion states of the others change, enabling different gear ratios.
Figure 1: Schematic Diagram of Planetary Gear Structure
II. Working Principle of Planetary Gears: How Do They Enable "Automatic Shifting"?
The key to the "automatic" shifting of an automatic transmission lies in the协同工作 of the planetary gear set with the hydraulic control system and clutches/brakes. The core principle is: by controlling the fixed or rotating state of different components within the planetary gear set, the power transmission path is altered, resulting in different gear ratios.
A basic planetary gear set can achieve four primary operating modes:
- Reduction Drive (Downshift)
- When the ring gear is fixed, power is input through the sun gear and output from the planet carrier. The system achieves speed reduction and torque increase. This is commonly used for vehicle起步 or climbing.
- Overdrive (Overdrive Gear)
- When the sun gear is fixed, power is input through the ring gear and output from the planet carrier. The system can achieve an output speed higher than the input speed ("overdrive"), used for highway cruising to lower engine RPM and save fuel.
- Direct Drive
- When the sun gear, planet carrier, and ring gear are locked together as a single unit, power is transmitted directly with a 1:1 gear ratio, offering the highest efficiency.
- Reverse Gear
- By changing the input component or the method of fixation—for example, fixing the planet carrier and inputting power through the sun gear to output from the ring gear—reverse rotation is achieved, enabling reversing.
Modern automatic transmissions typically use two or more planetary gear sets connected in series or parallel (e.g., Simpson, Ravigneaux structures),配合 multiple clutches and brakes, to enable 4-speed, 6-speed, 8-speed, or even 10-speed automatic shifting.
III. Main Applications of Planetary Gears in Automobiles
- Automatic Transmissions (AT)
- This is the most typical application scenario for planetary gears. Whether in traditional hydraulic automatic transmissions or modern CVTs (which simulate planetary gear functions via a belt and pulleys) and DCTs (Dual Clutch Transmissions), the core shifting logic借鉴了 the principles of planetary gearing.
- Differential
- The differential in the rear or front axle is essentially also a planetary gear structure. It allows the left and right wheels to rotate at different speeds when turning, preventing tire scrubbing. The "planetary gears" (also called differential pinion gears) in the differential rotate synchronously when moving straight and create a speed difference when turning.
- Hybrid Powertrain Systems (e.g., Toyota THS, GM Voltec)
- In hybrid vehicles, planetary gears are used in Power Split Devices (PSD). For example, Toyota's "Power Distribution Unit" (Planetary Gear Set in Hybrid Synergy Drive) intelligently分配 power from the engine, generator (MG1), and traction motor (MG2), enabling seamless switching between efficient engine operation and electric drive.