


The engine is the core of every car. Despite varying designs, its basic workings are universal. This guide decodes the engine through detailed diagrams and systematic explanation, offering an essential understanding of how your vehicle powers on.
Complete Engine Diagram
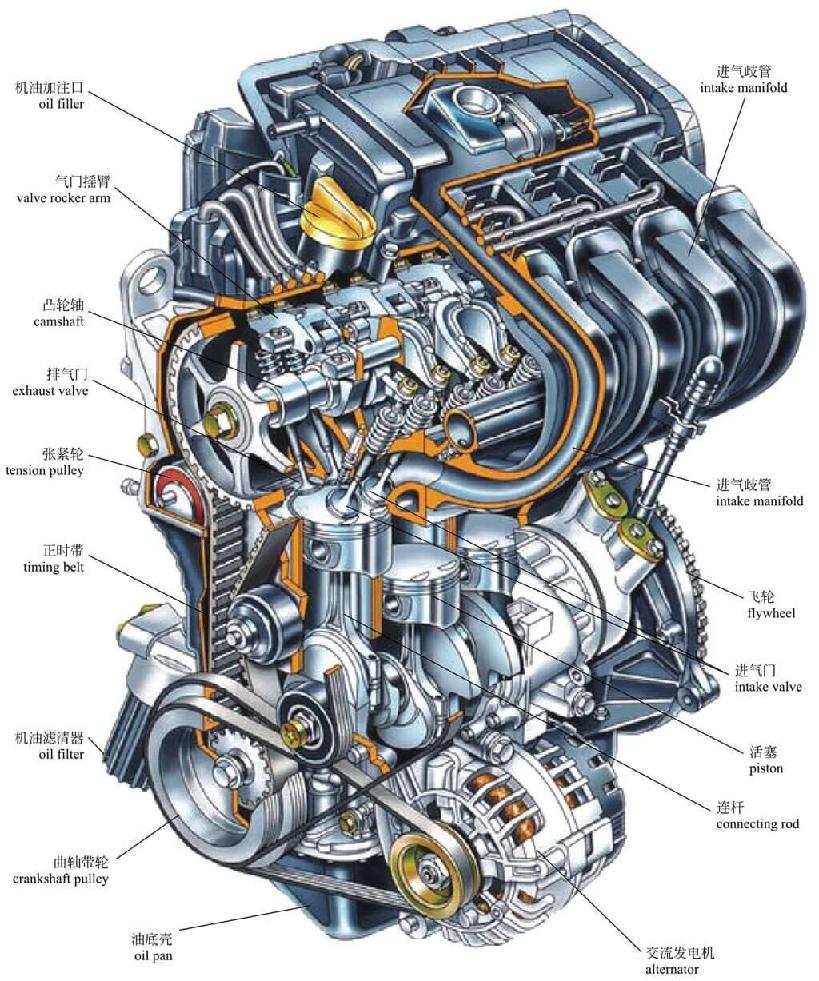
A typical automotive engine is composed of two major mechanisms and five primary systems:
Let's begin our illustrated breakdown of each component.
Crank-Link Mechanism
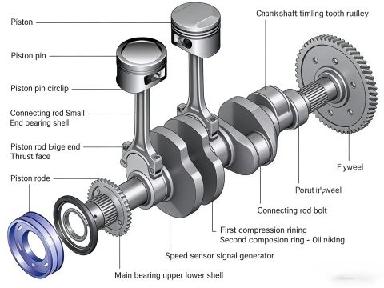
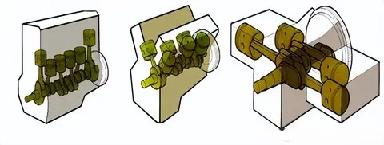
The crankshaft and connecting rod assembly comprises the cylinder block group, the crankshaft and flywheel group, and the piston and connecting rod assembly.
1. Cylinder Block Assembly
The cylinder block assembly forms the engine's core structure and includes the following key components: the cylinder block, cylinder head, head gasket, oil pan, valve cover (commonly known as the rocker cover), and the main bearing caps.
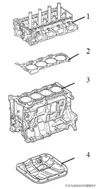
1—Cylinder Head
2—Head Gasket
3—Cylinder Block
4—Oil Pan
The cylinder block serves as the main structural framework of the engine. It integrates the cylinders and crankcase into a single unit, providing the foundational structure for mounting the crankshaft, pistons, and various other components and accessories.
Based on the arrangement of its cylinders, cylinder blocks are primarily categorized into three configurations: inline, V-type, and horizontally opposed (boxer).
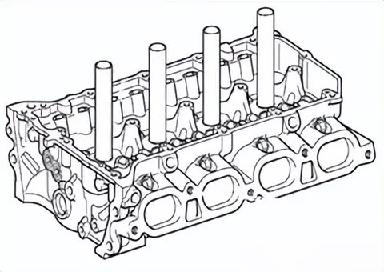
The cylinder head serves to seal the top of the cylinders. Together with the pistons, it forms the combustion chambers. It is designed to withstand the high temperature and pressure of combustion gases and also acts as the mounting platform for the valvetrain components.
Cylinder Head Gasket
Also known as the head gasket, it is situated between the cylinder head and the cylinder block. Its primary function is to ensure a reliable seal, preventing combustion gas leakage and coolant seepage from the water jacket.
Oil Pan
The oil pan forms the lower half of the crankcase, also referred to as the lower crankcase. Its purpose is to enclose the crankcase, serving as a reservoir for engine oil while preventing the ingress of contaminants.
Valve Cover
Located on the top of the engine, the valve cover is a protective casing mounted over the cylinder head. It provides a seal for the valvetrain compartment, safeguarding it against the entry of contaminants.
2. Crankshaft and Flywheel Assembly
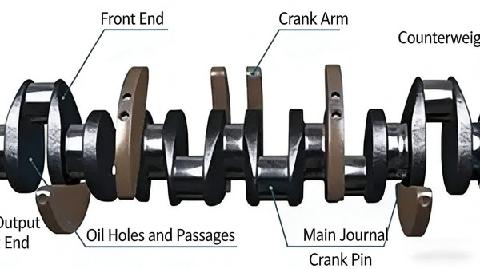
The crankshaft and flywheel assembly is primarily composed of the crankshaft, flywheel, crankshaft pulley, and timing gear(s). It is mounted onto the cylinder block.
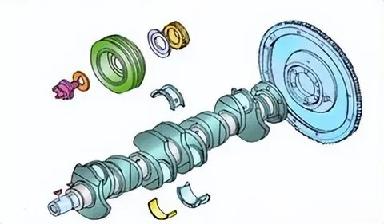
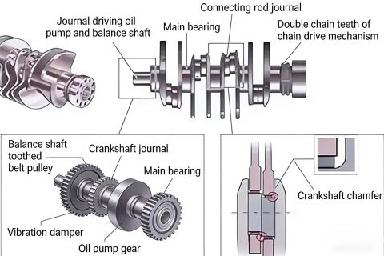
The crankshaft receives forces from the connecting rod, converts the reciprocating motion of the piston into the rotational motion of the crankshaft, and outputs it.
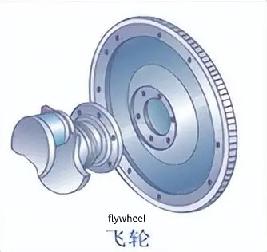
The flywheel is mounted at the rear of the engine. It has a certain weight and serves an energy-storage function. It also serves as the mounting component for the clutch, and its ring gear is the gear that drives the engine's operation.
The crankshaft pulley serves as the power source for driving other engine accessories. It transmits power through the drive belt to components such as the generator, water pump, compressor, and power steering pump. It is equipped with a damping or vibration reduction device to mitigate the impact vibrations generated during engine operation.

The crankshaft timing gear transmits power to the camshaft timing gear, ensuring stable engine operation.
1.Piston and Connecting Rod Assembly
The piston and connecting rod assembly primarily consists of the piston, piston rings, piston pin, connecting rod, connecting rod bearing shells, and connecting rod cap.
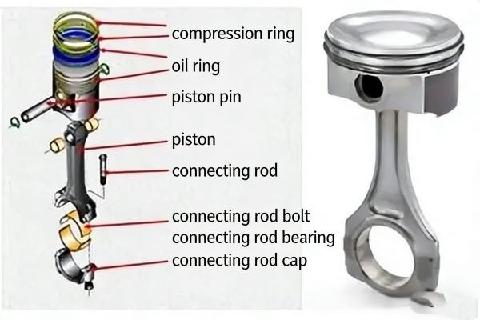
The piston is a component that undergoes reciprocating motion within the engine cylinder. The top of the piston constitutes a major part of the combustion chamber.
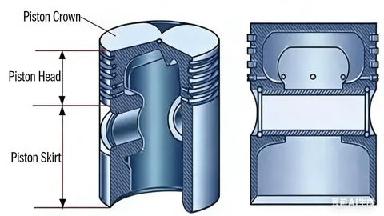
Piston Ring
A metal ring fitted into the grooves of the piston, divided into compression rings and oil control rings.
Piston Pin
Used to connect the piston and the connecting rod, transmitting the gas force acting on the piston to the connecting rod.
Connecting Rod
Connects the piston and the crankshaft, transmitting the force from the piston to the crankshaft and converting the reciprocating motion of the piston into the rotational motion of the crankshaft.
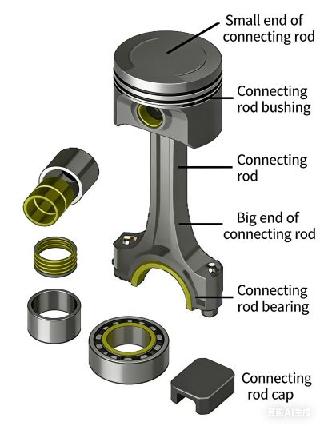
Connecting Rod Bearing
Installed at the joint between the connecting rod and the crankshaft, it serves functions such as wear resistance, connection, support, and power transmission. The bearing wall is equipped with an oil passage hole.
Connecting Rod Cap
It houses the connecting rod bearing and secures the connecting rod to the crankshaft via connecting rod bolts.
Connecting Rod Bolt
Functions to lock the connecting rod cap and the connecting rod together.